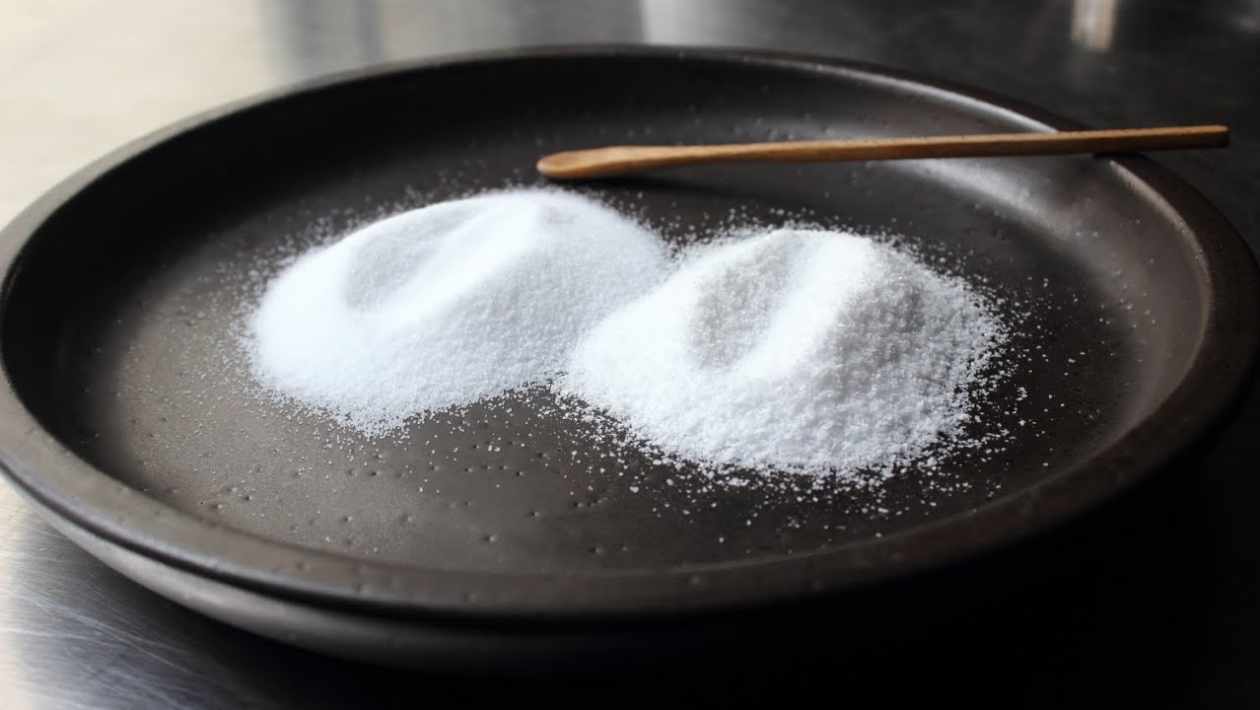
It is becoming more common to find recipes that indicate kosher salt among their ingredients, especially you can see it in blogs outside our borders. You may be curious to know what is kosher salt and how it is different from common salt.
As you surely already know, kosher (or kosher ) is a Yiddish term (Jewish or Hebrew) that means ‘pure,’ as we indicated in the post on Kosher Wine precepts of Judaism. I can have food to consider in using kosher salt. It must go through a series of processes faithful to the Jewish religion. And these foods are those that can consumed by those who profess this religion. So, let’s know more what is kosher salt.
What is kosher salt?
Kosher salt is not iodized or fluoridated. It mainly uses to treat kosher meat and extract the blood in the kashrut process(Another of the Jewish food laws is that they cannot eat anything with blood). It is coarse salt, and sometimes we get it flaked. They claim it tastes cleaner than regular salt. Thats why many North American and English chefs are adopting kosher salt for cooking.
At first, the problem may be the difference in flavor and volume when adding the dishes since not all kosher salts have the same thickness. Another problem is using it in cakes or other preparations because it does not dissolve well in small amounts of liquid. We must also consider the iodine that we introduce into our diet through other foods before switching to kosher salt.
We do not know if kosher salt is already running in national kitchens. Have you tried it? Do you find exciting differences?
It will be challenging to find a kitchen in a world where there is no salt pinch. It is an essential element of world gastronomy, whose function is to enhance the flavor of food.
But it is much more complicated than we think because it also increases or decreases the capacity of other senses involved in the appreciation of taste. For example, it softens the bitters’ impact, but only if this taste and the salty mix before putting them in the mouth.
Admittedly, salt is salt, and most of us cannot appreciate all the taste differences of the varieties that exist. It requires an excellent palate to blindly distinguish a Himalayan salt from another from Hawaii and a lot of gastronomic knowledge to learn to use them most appropriately.
Uses of Kosher salt: what is kosher salt?
It is logical because you can hardly find more than one type of salt in grocery stores until recently. But little by little, as gastronomy has risen in the scale of cultural interests, new ways of seasoning dishes have become famous without us being clear on many occasions what salt use for what.
That is what this article is about, to find out why we pay around one euro for a kilo of common salt while Es Trenc fleur de sel, from Mallorca, costs 55 euros per kilo. And it’s probably not the most expensive in the world.
The first difference between the two is their origin. The second, how it treats and the amount of each market. So from the outset, you can distinguish between industrial and artisanal salt.
Choosing between one and the other depends on what it is going to uses for. To salt food in general, it is not necessary to resort to one of those varieties that have become so fashionable, such as pink Himalayan salt or Maldon. These should reserve to give a special touch to the dishes.
Different Types of Salt: What is Kosher salt?
All salt is quite similar in composition which is sodium chloride. It comes in different forms, from tiny granules to crystals of various sizes and scales. This salt is the main component of seawater, and for thousands of years, it has uses as a food preservative.
There are also salt mines halite. It formed by salt chloride and various minerals. It is usually thicker than marine and has more impurities, which must remove because some mineral remains are not edible.
Sea Salt
The sea salt obtains by evaporation of saltwater. It is usually more refined and less concentrated, making it easier to control the amount used for each stew. This salt has complex flavors that depend on the area of origin. The way it picks or “harvested,” and its morphology. It provides minerals such as calcium, magnesium, and copper.
Table Salt
Table salt is the most common. It is the most industrialized, and most of what market contain added iodine to increase iodine deficiency. This salt usually undergoes a refining process, which extracts any trace of mineral. It treats so that it does not cake in humid environments, which gives it a slightly metallic taste.
It is the most useful in domestic kitchens, where that subtle difference in taste not appreciates. But it does not prefer among professionals in haute cuisine. It is the cheapest and easily dissolve and integrated into preparations.
Flower Salt
Female chef seasoning a steak on a grill.
The flower of salt, or “caviar of salts,” is one of the most appreciated and expensive sea salts in the world. The name gives to the tiny flake- shaped crystals. That form on the surface of saline deposits after a short period of crystallization. Its price is justified both by its scarcity and by the traditional manual system of collecting it, with wooden rakes.
The Mallorcan flower of salt already mentioned in this article comes from the natural park. It located to the southeast of the island, which the Phoenicians discovered in the 4th century BC. And which has exploited by several generations of islanders.
The flower of salt, or “caviar of salts,” is one of the most appreciated and expensive sea salts in the world.
In Fuerteventura, some historic salt flats have also preserved. Those of Carmen, on the coast of Antigua, prepare salt from the foam left by the waves when they hit the facilities’ breakwater.
This salt does not usually use for cooking, but to give a final touch to dishes. It blends easily with food and gives it a very pure and delicate salty. However, it is suitable for any word, be it meat, fish, or vegetables. Also for salads and cold preparations. Even for desserts, including chocolate, with which it combines very well.
Sal Maldon
It collects in the estuary of the River Blackwater, in Essex, in England. The country where the salt forms thin layers similar to fish scales. We get it as mined and processed by hand for thousands of years. This salt gives a final touch to dishes. Especially when you want to provide a crisp point to grilled meat, vegetables, fish, biscuit foie grass, or cold appetizers. It only added a few moments before serving to prevent it from dissolving in the heat of the food. And it remains on the palate for a long time.
Himalayan pink salt
It comes from the Khewa mines in the Pakistani area of that mountain range. Its pink color distinguishes it. Which can range from a paler tone to an intense pink depending on the depth.
Himalayan pink salt can go from a paler shade to deep pink, depending on how deep it has found.
It is very rich in minerals, so it contains 84 parts of the human body. And because of this, it has much more intense. Also complex flavor than any other salt in our kitchens. Its grains can keep the heat for hours, so in some cases, they help to cook delicate foods such as fish. The grains are coarse and irregular, and some preparations require pre-grinding.
Black salt or Kala Namak
It is a variety of rose from Nepal, to which a mixture of aromatic herbs and spices added. And it kept on a charcoal fire for a whole day. The result is a dark salt with a robust, almost sulfurous flavor. It recommended for typical dishes of the region and seasoning avocados and mangoes. It takes getting used to its smoky and full flavor.
Coarse salt
It is usually of marine origin, but it is used differently from the fine one since it has a higher sodium chloride concentration. As the grains are so large, it is not suitable for dishes that require them to easily integrates.
You can use it like the scales or the Himalayan to finish a dish, but it is less delicate and subtle than these. Precisely because of how long it lasts without falling apart, it is the most suitable for marinating or making meats, vegetables and fish with salt.
Coarse salt is more suitable for marinating or making salted meats, vegetables, and fish.
Persian blue salt
Rich in minerals, it is extracted from a lake in Iran. Its particular color is due to its minerals and the natural pressure that causes the sun to reflect differently.
Subtly sweet, it gives off a citrus aroma that makes it very suitable for fish en papillote and tomato-based preparations and to decorate the glasses of cocktails that require it.
Celtic or gray salt
It obtains in saline deposits in which the tidal water deposited in the USA. It is rich in magnesium, calcium, and potassium. Also, its alkaline pH contributes to the assimilation of sodium by the body. It has an intense mineral flavor. It goes well with fish and meat.
Hawaiian salt
It comes from that Pacific island and has a volcanic origin. The pink, which comes from the mixture of seawater with volcanic mud. And the gray, which owes its hue to the activated carbons present in the lava, are known.
Gray is especially recommended for pork, although it can season other meats, fish, and poultry, always as a final touch.
In its flavor, a smoked aftertaste appreciated. Gray is especially recommended for pork, although it can season other meats, fish, and poultry, always as a final touch. The rose is more aromatic and combines with salads, seafood, and, due to its color, it gives a charming aesthetic touch to the cocktail glasses.
FAQ of what is Koher salt
-
What is the best salt in the world?
Both sea salt and Himalayan salt have the balance of minerals we need. And they have the right ratio of potassium and sodium which is good for our body. Other types of salts are also available in natural and crystal.
- Why is iodine added to salt?
Salt contains iodine, essential for life. This element helps us produce thyroxine, an essential hormone for life that allows us to transform calories into energy.
-
What is the most harmful salt?
Sea salt is just as harmful as common salt. When it comes to nutrition, the only difference between sea salt, rock salt, and ordinary table salt is that the first two are much more expensive than the third.
- Why is refined salt terrible?
However, they add, the main consequences of seasoning dishes with refined common salt can be hypertension problems, hardening of the blood vessels, menstrual discomfort, or feelings of exhaustion.
Conclusion of what is kosher salt
It has been introduced in professional kitchens, and from there to domestic ones, due to its purity. Since iodine is rarely incorporated, and its low salinity. Although you have to be careful when using it, add it in pinches because it is somewhat thick, and it is difficult for it to dissolve, it is easy to overdo the dose.
It is suitable for meats because it adheres and spreads nicely over the surface. If you want to give texture and a crunchy touch, you can add it when serving.