You should understand about systolic Vs Diastolic pressure if you expect a healthy life. Systolic and diastolic blood pressure ratio is an analysis that is done first when you visit your doctor for a check-up. It is easy to do, and it is not time-consuming at all. But it gives a decent idea about how your heart is functioning.
The heart contains two muscular pumps working in series, wrapping with a transparent sac which permits free movement with each heartbeat and respiration. The heart sends blood to both lungs and body. The right ventricle pumps blood to the lung, and the left ventricle pumps blood to your whole body. Your heart has four chambers and four valves. The valves distinguish the sections from each other and letting the blood run through the rooms and into and out of your heart. Your heart beats about 60 to 100 times per minute.
The high pulse rate is tachycardia, and a low pulse rate is a bradycardia. Both situations are hazardous to health. Blood pressure is an essential guide to cardiovascular risk and provides critical knowledge about the seriously ill and injured patient. Blood pressure often varies. It rises with stress, excitement, and atmosphere. The blood pressure of a person increases only by seeing a healthcare worker is called white coat hypertension. This happens out of tension around doctors. So let’s find out about systolic Vs diastolic pressure.
Systolic Vs diastolic Blood Pressure:
For understanding systolic and diastolic pressure firstly, you have to know what systole is and what diastole is. Diastole is when the heart muscle dilates and makes room for blood, which is returning from all over the body. So during diastole person’s blood pressure decreases.
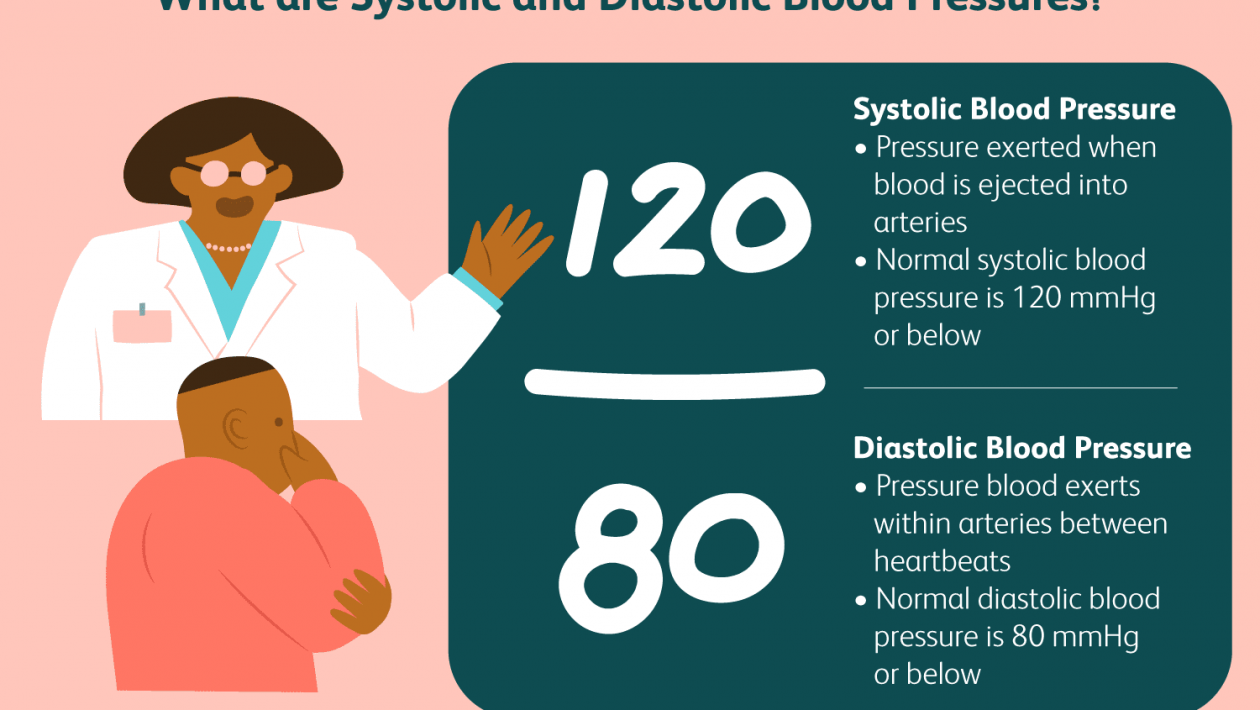
Systole is the contraction of the heart muscle. When heart contracts, it send the blood into the large blood vessels of the body. From there, blood goes to all over the body and vital organs. During systole, a person’s blood pressure increases.
Blood pressure is a measure of force that the circulating blood exerts against the arterial wall. Systolic blood pressure is the maximum pressure that occurs during the contraction of your heart. Diastolic blood pressure is the lowest value that occurs during the relaxation of the heart. Both systolic and diastolic pressure is maintained by the elasticity and compliance of the vessel wall.
Blood Pressure is measured in mmHg unit and recorded as systolic blood and diastolic blood pressure, together with where and how the reading was taken, for example BP: 146/96 mmHg right arm, supine. That’s how doctors record and compare systolic Vs diastolic pressure.
How to examine a patient with high or low blood pressure:
You should make a blood pressure chart. It’s essential to evaluate blood pressure regularly because it fluctuates over the course of the day and also relies on the atmosphere. It can also vary due to things like physical exertion, vigorous exercise, anxiety, pain, or extreme heat or cold surroundings. But this is interim, and it soon returns to normal.
It doesn’t inevitably mean that you have high blood pressure after getting it high once. Going to the doctor makes some people so uncomfortable that their blood pressure goes up in some cases. So at least measuring it two times is necessary to find out if you actually have high blood pressure or not.
Blood pressure is assessed by means of an appliance called a sphygmomanometer. A doctor or nurse will evaluate your blood pressure using a small meter attached to an inflatable cuff. But don’t worry, it is straightforward and painless.
Also
The person who is assessing your blood pressure fastens the cuff around your upper arm. Some cuffs are used in the thigh in the case where the is very lean and thin or in case of children. For children, there is a smaller cuff. Your medic will place a stethoscope over an artery near the elbow to listen to the blood shifting through your street .then your doctor will inflate the cuff to a pressure higher than your systolic blood pressure and slowly release it.
The first sound that is heard through the stethoscope implies the systolic blood pressure. The sound is similar to a whooshing noise. And at the point when the noise began to disappear, it denotes the diastolic blood pressure. In certain situations, such as the intensive care unit, it is measured invasively by entering a catheter into an artery. However, in favorable position, healthcare workers estimate blood pressure following the below- procedure:
- Ease the patient for five minutes
- Measure the blood pressure in both arm
- Search the pulse rate
- Examine eye to find out any abnormality
- Assess the heart
- Look for evidence of heart failure.
There is some common problem during BP measurement:
- Wrong cuff size. It is most common in obese and younger patients. There are different cuffs to measure blood pressure by ages.
- BP is different in each arm.
- Excess pressure of the stethoscope can artificially lower the diastolic pressure. The systolic pressure is usually not affected.
- Patients are at the wrong place can give you a false result. The patient’s arm should be level with his heart.
- Postural change is falling on the blood pressure after standing up suddenly.
Theses procedure helps the doctors to record systolic Vs diastolic pressure.
What are the physical signs you look for:
- Puffy face
- Central obesity with the red moon face
- Excess hair all over the body including face
- Pulse
- Anemia
- Swelling of the leg, face stomach
- Kidney enlargement
- Eye
- Bedside urine examination
Your blood pressure may be familiar, high, or low, depending on your bodily condition. An abnormal elevation of blood pressure is called Hypertension. And if blood pressure decreases below the average level, then its called hypotension.
British Hypertension society classification of blood pressure is given below:
- Optimal: less than 120 systolic and 80 diastolic.
- Normal: less than 130 systolic and 85 diastolic
- High normal: less than 139 systolic and 89 diastolic
Gradewise classification of Hypertension:
- Grade 1(Mild): 140 to 159 systolic and 90 to 99 diastolic
- The Grade 2(Moderate): 160 to 179 systolic and 100 to 109 diastolic
- Grade 3(severe): more than 180 systolic and less than 110 diastolic
Hypertensive emergency:
Hypertensive emergency or hypertensive crisis implies an extreme elevation of blood pressure with organ dysfunction. It includes symptoms like headache, irritability, confusion, altered mental status, blood in the urine. Also, It is a severe condition, and you should seek treatment as early as possible.
Hypertensive urgency:
It is a life-threatening condition. Here BP rises to more than 220 systolic and 125 diastolic. In this stage, hospitals ization is a must.
Risk factors:
Your gender is a significant risk factor for elevated blood pressure. Naturally, men are at a higher risk of high blood pressure due to their strenuous lifestyle. Women are at lower risk until age 65 years. Other risk factors are:
- A family history of blood pressure is a significant risk factor. If you have a first-degree relative who has high blood pressure, you are more likely to carry the disease.
- Africans are most likely to have high blood pressure.
- Obesity
- Diabetes
- High cholesterol
- Previous kidney disease
- Hormonal imbalance
- Menopause
- Smoking
- Chronic stress
- Sedentary worker
- High fat and high sugar diet
- Salt intake
Some drugs are also responsible like:
- Alcohol
- Oral contraceptive pill
- Steroid
- NSAID
- Erythropoietin
- Sympathomimetics
Sleep apnea is another risk factor for high blood pressure that’s someone doesn’t notice quickly. In this condition, you may stop breathing or have ineffective breathing throughout sleep.
Your oxygen levels fall when your breathing is not adequate and your blood vessel continues to constrict. This elevates your blood pressure. Increased blood pressure may continue during the day when breathing is normal in persistent sleep apnea. Proper treatment is needed in sleep apnea; otherwise, the life-threatening condition may arise.
Hypotension:
Hypotension is a condition when your blood pressure falls to less than 100 systolic and 60 diastolic. Various reasons are behind this condition. They are stated below:
- Anemia
- An injury that causes severe bleeding
- Piles
- Excess bleeding during period
- Thyroid dysfunction
- Hormonal imbalance
- Parkinsons disease.
- Dehydration
- Diarrhea
- Vomiting
- Worm infestation
- Malaria
Orthostatic hypotension or postural hypotension is another entity that denotes a condition in which your blood pressure drops when you move from sitting to standing. It is common in older age.
Symptoms of high blood pressure:
A hypertensive patient is almost symptomless unless any vital organ is involved. However, there are some symptoms that are related to Hypertension. They are:
Dizziness
Breathlessness
fainting
Headache
seizures
Restlessness
chest pain
Abdominal discomfort
falling
Tinnitus
loss of balance
nausea
Vomiting
thirst
Confusion
inability to concentrate
headaches
blurred vision
Lassitude
fatigue
shallow breathing
shortness of breath
clammy skin
Pale skin
bluish-tinged skin
A complication of Hypertension:
There is some life-threatening severe complication that may arise:
- Heart Attack
- Heart failure
- Kidney failure
- Eye disturbance
- BlindnesEncephalopathyhy
How often should I check my blood pressure:
You should know about your systolic Vs diastolic pressure to combat serious illness. If your blood pressure is normal (less than 120/80), yearly checking is enough.
However, if blood pressure is increased — systolic blood pressure between 120 and 129 or diastolic blood pressure of less than 89 you should check 3-6 monthly.
If you have stage 1 hypertension — 130-139 over 89-90 — you should check it monthly. Your doctor may suggest you do lifestyle modification, or he may start low dose medications. With monthly checking, your doctor will also do some blood tests and urine tests to find out any underlying condition.
In stage 2, Hypertension — 140/90 or higher — medication is a must with more frequent checking.
Who needs treatment:
The following patient needs treatment as early as possible.
- Who has malignant Hypertension?
- All patients with sustained systolic BP more than 160 or diastolic BP more than 100 mmHg.
- Patient with systolic BP 140 to 159 mmHg.
- Diastolic BP 90 to 99
- Patients with isolated systolic Hypertension
How to treat Hypertension:
Non-drug treatment:
Lifestyle modifications are essential as the first step in treating any stage of high blood pressure. These are:
- Salt restriction
- Smoking should be stopped
- Weight reduction in the obese patient
- Low fat and saturated fat is useful for treating high BP
- Increase intake of fruits, vegetables and also oily fish
- Also, Reduction of anxiety and tension
- Control of diabetic
- Restriction of tea and coffee
- Restriction of alcohol intake
- Also, Control of other modifiable risk factors
Drug Treatment:
- Diuretics
- ACE inhibitor
- Alpha-blocker
- ARB
- Combined alpha and beta-blocker
- Renin inhibitor
- Methyldopa
Take home note:
However, diastole and systole are two different stages of the cardiac cycle. When heartbeats systole and diastole occurs. When the heart contracts to pump blood out systole occurs, and diastole occurs when the heart dilates after contraction. A person who fears that they have high or low blood pressure should consult their doctor to find out the best treatments, including medications or lifestyle modifications. When a person going through treatment for problematic blood pressure, they should measure their blood pressure levels regularly, whether there is a symptom or not.
High or low blood pressure is mostly manageable if you switch to a healthy lifestyle. For high blood pressure, healthy lifestyles, proper diet, regular exercise may help. If your blood pressure is persistently high, you have to take medication. Regular checking will help you to monitor your blood pressure. For low blood pressure, identifying the cause is significant and follow through any recommended treatment plans. I hope the above discussions will help you to understand systolic Vs diastolic pressure.
FAQ(frequently asked questions):
1.If high blood pressure is dangerous?
Ans: If you can control your blood pressure to a standard limit by medication and lifestyle modification, it is not dangerous. But you have to check it regularly.
- What is the usual range of blood pressure?
And: The usual range of blood pressure is 120 to 139 mmHg systolic and 80 to 89 mmHg diastolic.
- What is the most common cause of high blood pressure?
Ans: The most common cause of high blood pressure is unknown. But there is a correlation with diabetes, kidney disease, etc.